







Wisdom Panel™ Complete for Cats
£71.24
£94.99
Your cat’s health doesn’t have to be a mystery. With the world’s most comprehensive cat DNA test, you’ll get a full breed report, extensive health insights (including drug sensitivities and bleeding tendencies), and more. So you can deliver the kind of personalised care your cat deserves.
Includes:
Ancestry
Health
Traits
Results Within 3-4 Weeks
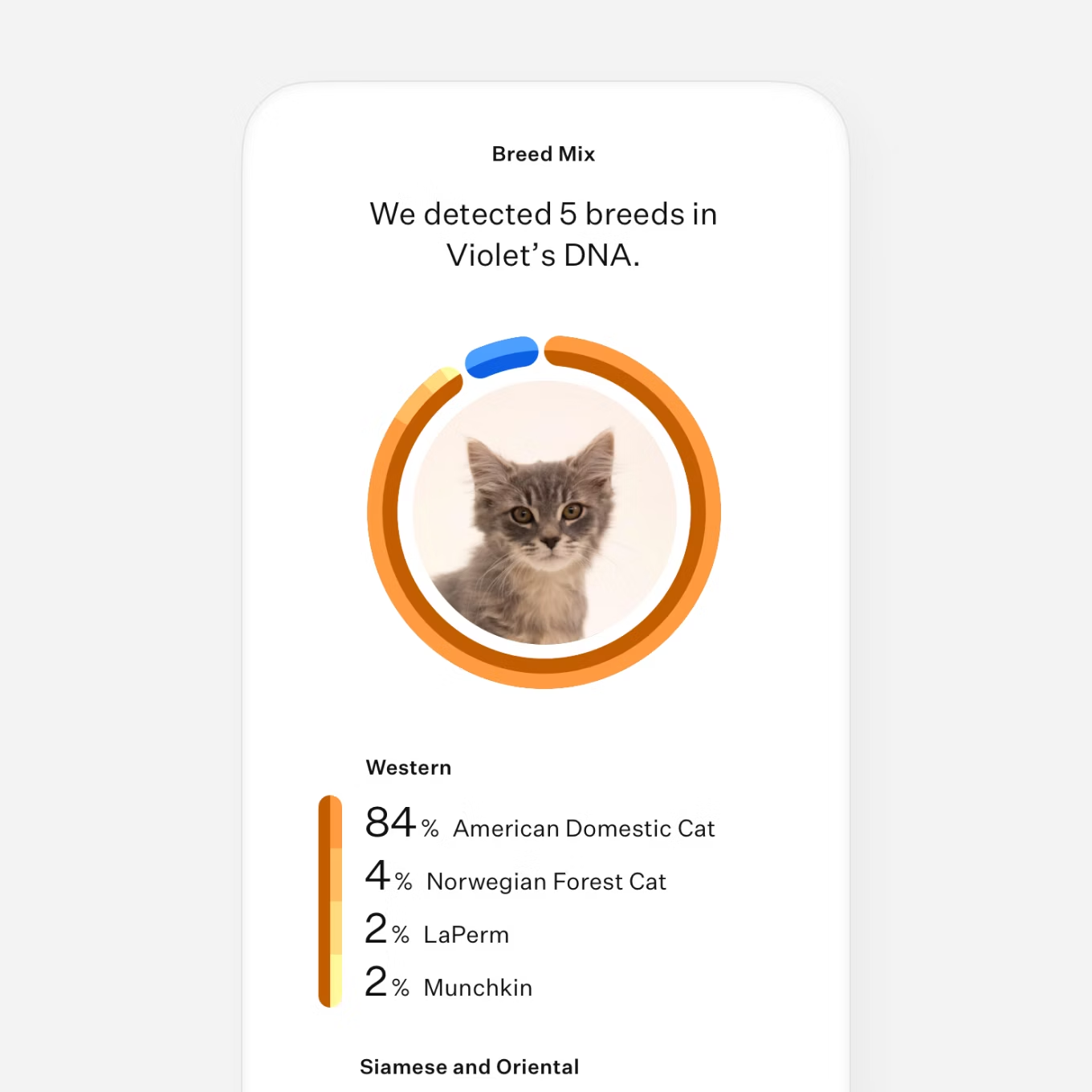
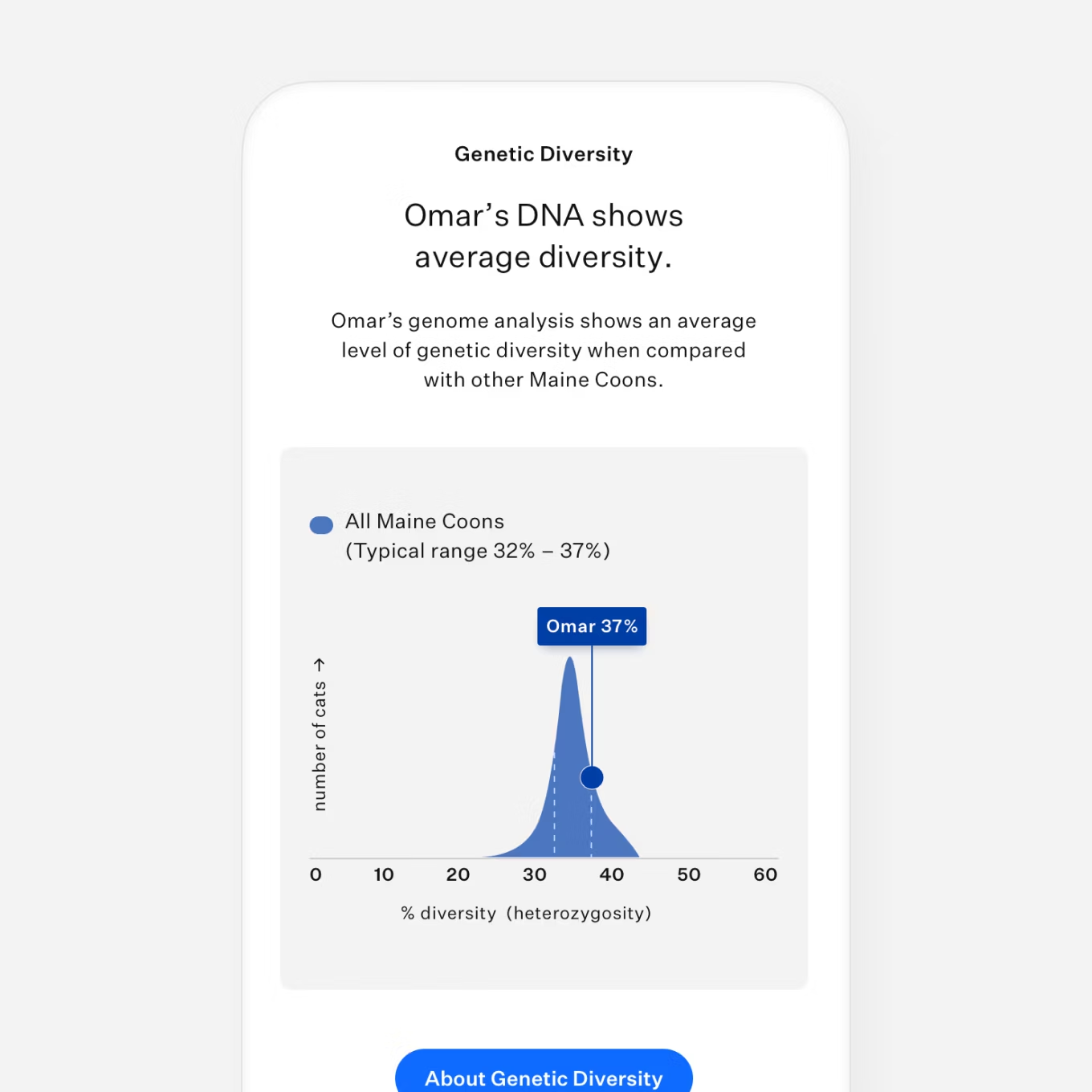
Screens for 70+ breeds and populations
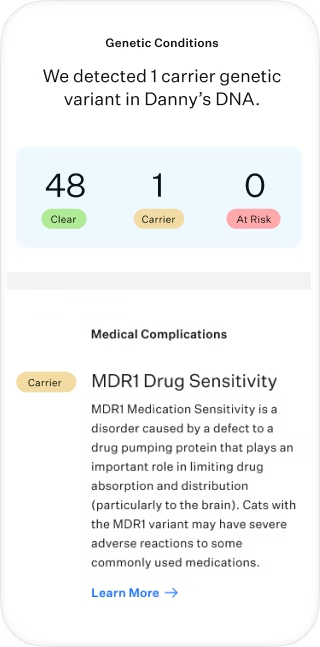
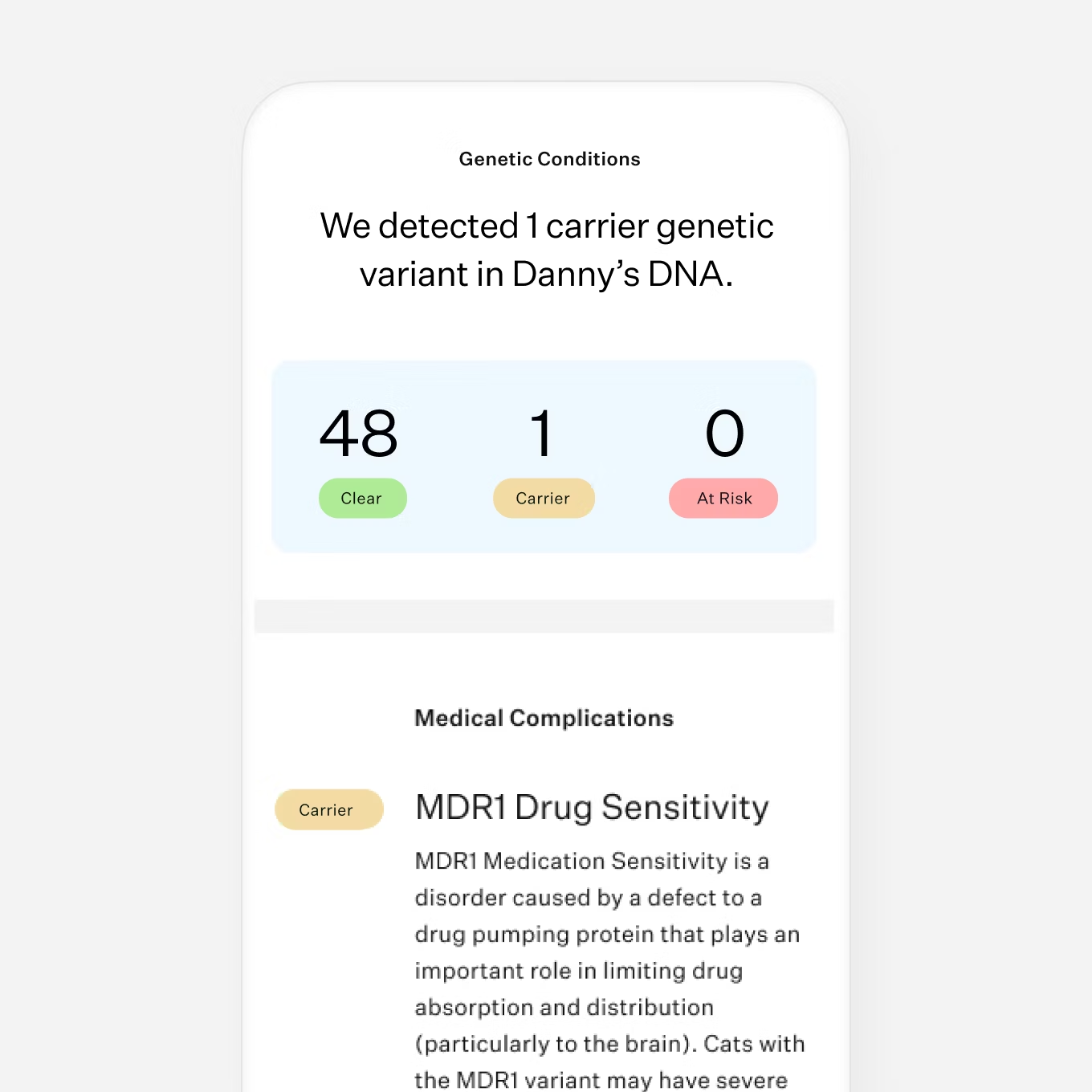
Test for 45 genetic health conditions
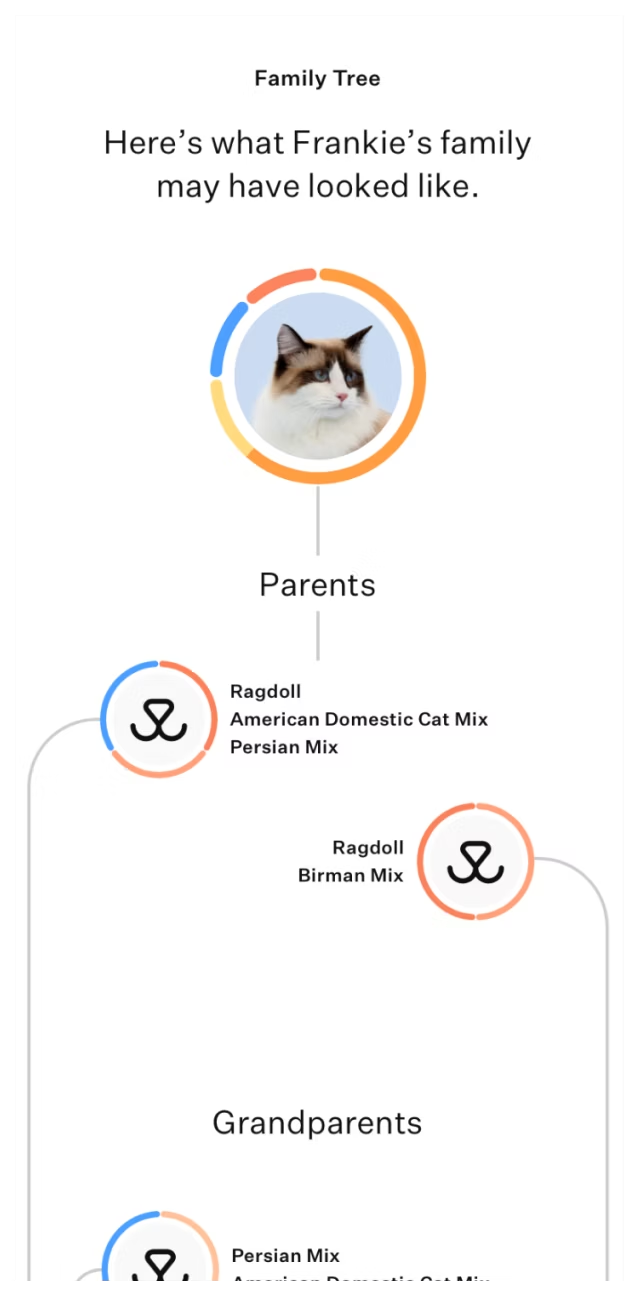
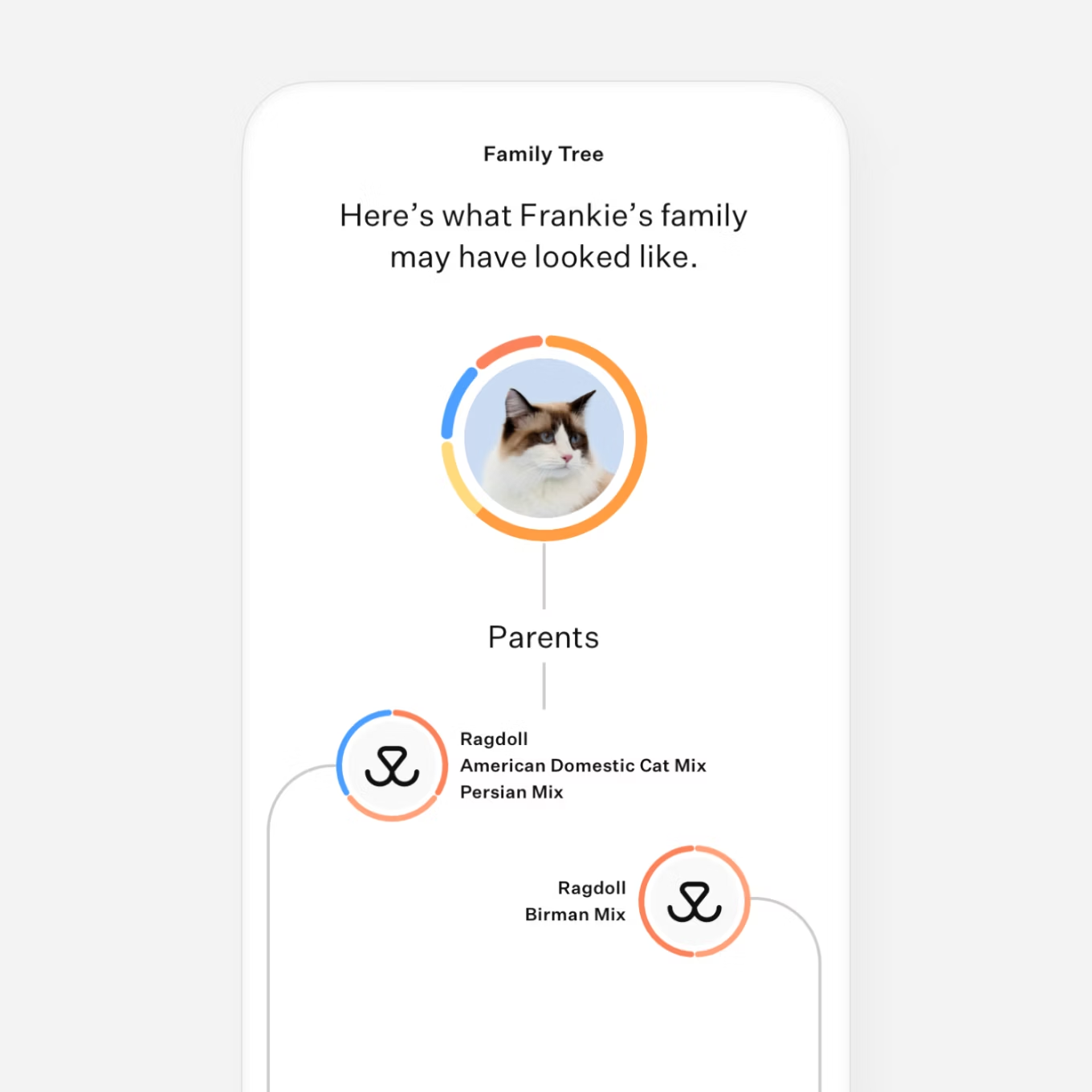
See a multi-generational family tree
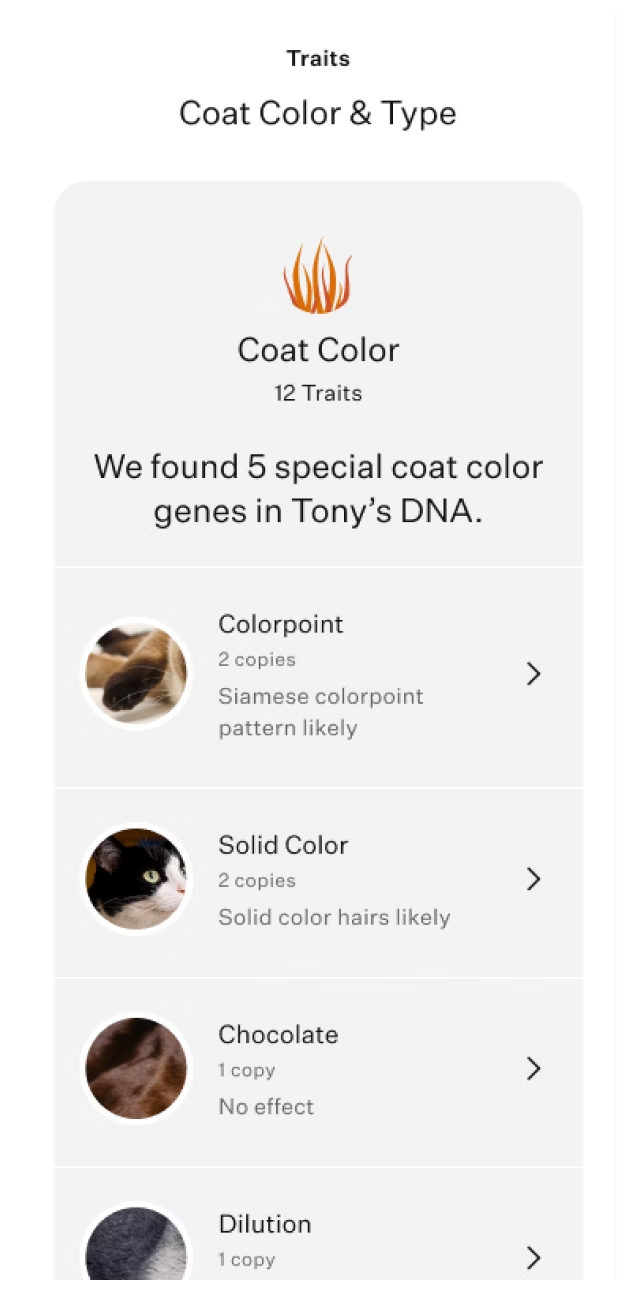
Test for 25+ physical traits
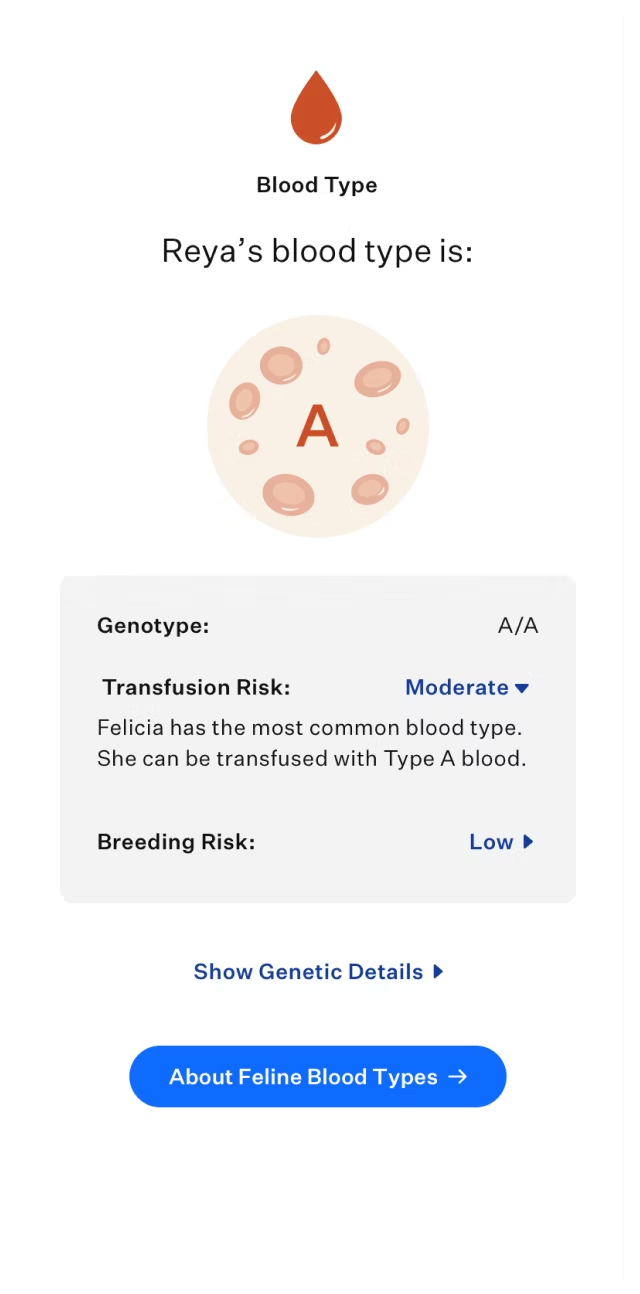
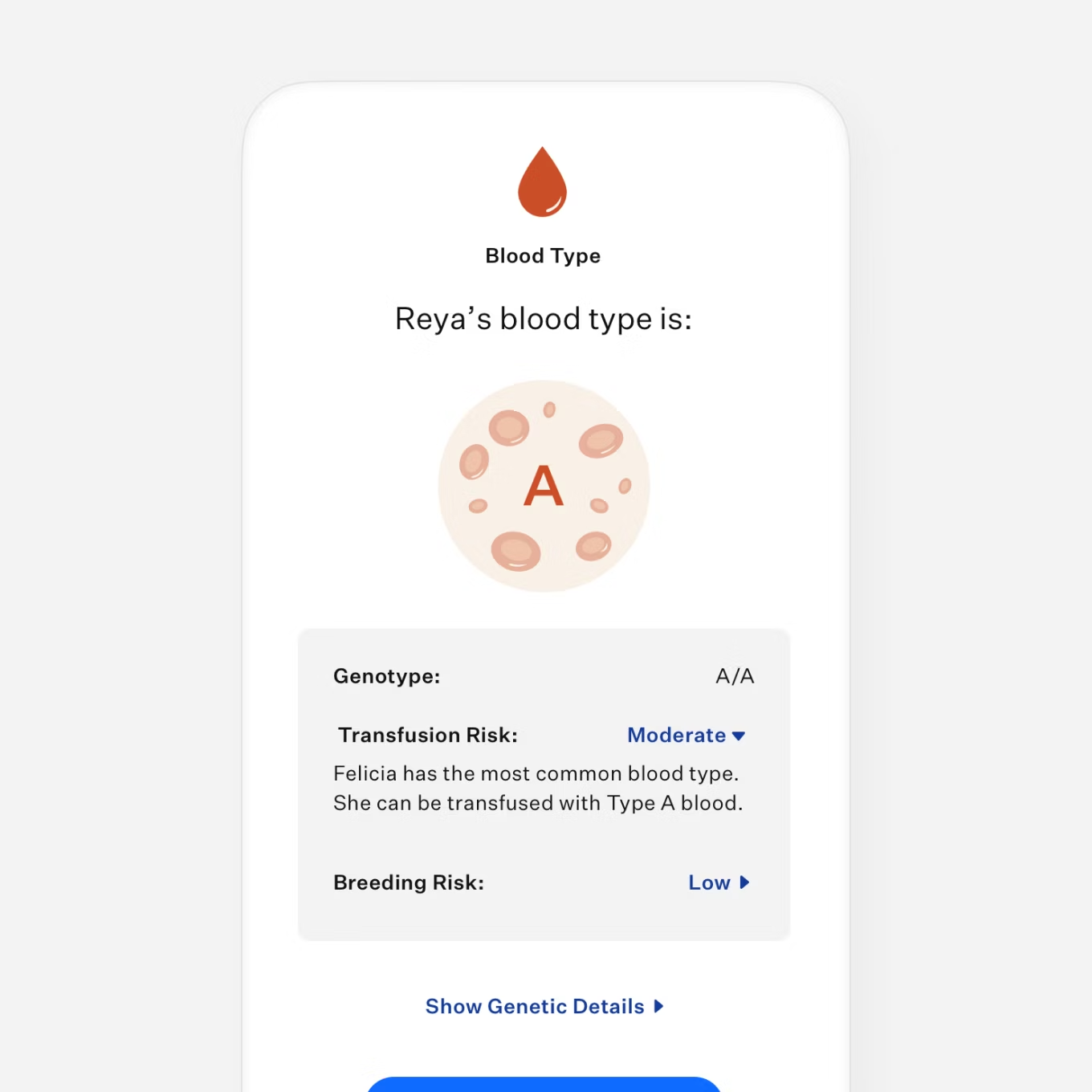
Identify blood type
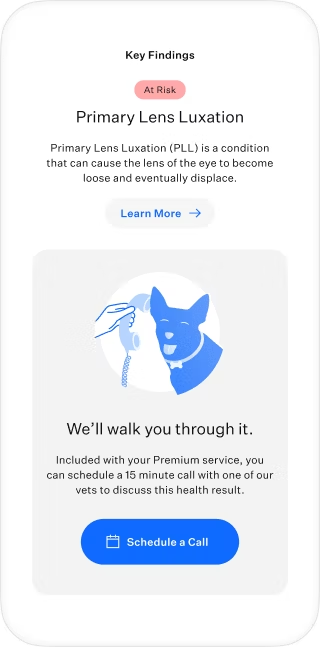
Genetic consult for 'at risk' health findings
Standard Delivery (2-3 business days). Orders are only fulfilled on business days and generally ship from the warehouse on the next business day. Should you choose to cancel an order before shipment please call our customer care line at 0808-1346-408.






Wisdom Panel™ Complete for Cats
£71.24
£94.99
Your cat’s health doesn’t have to be a mystery. With the world’s most comprehensive cat DNA test, you’ll get a full breed report, extensive health insights (including drug sensitivities and bleeding tendencies), and more. So you can deliver the kind of personalised care your cat deserves.
Includes:
Ancestry
Health
Traits
Screens for 70+ breeds and populations
Test for 45 genetic health conditions
See a multi-generational family tree
Test for 25+ physical traits
Identify blood type
Genetic consult for 'at risk' health findings
Standard Delivery (2-3 business days). Orders are only fulfilled on business days and generally ship from the warehouse on the next business day. Should you choose to cancel an order before shipment please call our customer care line at 0808-1346-408.
4 Easy Steps. One Comprehensive Report.

Activate

Collect

Send
Results
It's like magic, but pure science.
Get the knowledge you need to give them the care they deserve.
What makes Wisdom Panel™ the best choice?
Others
You should receive your results 3-4 weeks after our lab receives your pet’s DNA sample. We’ll send you an email when your results are ready. Please note: due to the digital nature of our product your results will be available in your online account only. No physical report will be mailed.
You can follow the progress of your DNA sample online with our test tracker. To see the tracker, log into your account and click on the status of the sample in question.
For most Wisdom Panel™ results, the option to download and print a Technical Report is available by visiting your pet’s “highlight” tab. At the bottom of that page, you’ll find a button that says "Download Technical Report".
It can. The report will always default to the gender of the cat that was entered at activation, but we are able to see the cat’s genetic gender in the raw data.
Yes! Wisdom Panel™ Complete for Cats can be used at any stage in a cat’s life. That said, we recommend waiting until a kitten has been weaned to prevent cross-contamination from skin and other cells within the mother’s milk.
Meet Reya.
Reya’s Wisdom Panel™ Complete for Cats test revealed that she could have adverse reactions to common medications. Now that her humans know, they can work with their veterinarian to support Reya’s safety during routine procedures. Find out what else her DNA had to say.
See Reya's Results
Learn about their genetic health & traits Cats can’t talk, but their DNA can.™ We test for 45+ genetic health conditions and 25+ traits so you can know them on an even deeper level.